The following is a conjugate heat transfer (CHT) optimization case for circular cross section U bend channel. This channel represents a heat exchanger for an electric aircraft.
Case: Heat flux and pressure loss optimization for U bend cooling channel Geometry: Circlar cross section U bend channel Objective function: Combined total wall heat flux and total pressure loss Design variables: 108 FFD points moving in the x, y, and z directions Mach number: 0.015 Reynolds number: 2.8e4 Mesh cells: 670,000 (fluid), 118,000 (solid) Solver: DASimpleFoam (fluid), DAHeatTransferFoam (solid)
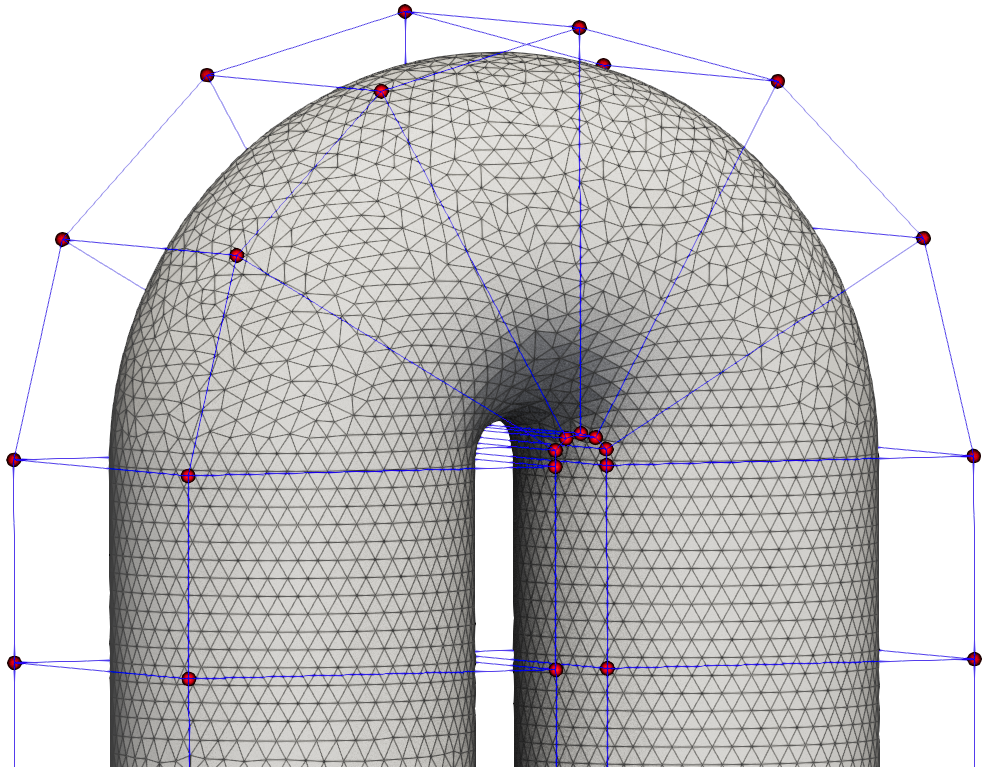
Fig. 1. Mesh and FFD points for the CHT U bend channel case
For this dual-solver case we first use the DASimpleFoam solver on the fluid domain, including all three parts of the objective function. The objective function is a weighted sum between pressure loss (TP1 and TP2) and total wall heat flux (Tmean). In this tutorial, the average outlet temperature (Tmean) is used to measure the heat flux performance. The final fourth block, HFX, only prints the total heat flux to the terminal from the fluid side of the CHT interface but is not used itself in the objective function (hence it is not added to the adjoint).
"function": {
"TP1": {
"type" : "totalPressure",
"source" : "patchToFace",
"patches" : ["inlet"],
"scale" : 1.0,
"addToAdjoint" : True,
},
"TP2": {
"type" : "totalPressure",
"source" : "patchToFace",
"patches" : ["outlet"],
"scale" : 1.0,
"addToAdjoint" : True,
},
"Tmean": {
"type" : "patchMean",
"source" : "patchToFace",
"patches" : ["outlet"],
"varName" : "T",
"varType" : "scalar",
"component" : 0,
"scale" : 1.0,
"addToAdjoint" : True,
},
"HFX": {
"type" : "wallHeatFlux",
"source" : "patchToFace",
"byUnitArea" : False,
"patches" : ["ubend_inner"],
"scale" : 1.0,
"addToAdjoint" : False,
},
},
The solid domain solver again has heat flux (from the solid side of the CHT interface) only printing to the terminal. The objective function is weighted as 90% for heat flux and 10% pressure loss.
"function": {
"HFXsolid": {
"type" : "wallHeatFlux",
"source" : "patchToFace",
"byUnitArea" : False,
"patches" : ["ubend_inner_solid"],
"scale" : 1.0,
"addToAdjoint" : False,
},
},
To run this case, first download tutorials and untar it. Then go to tutorials-main/UBend_CHT and run the preProcessing.sh script to download the mesh. Once that completes, run the optimization using the following command:
mpirun -np 72 python runScript.py 2>&1 | tee logOpt.txt
This case ran for 20 iterations, enhancing the total heat flux by 2.29% and decreasing pressure loss by 52.71%.
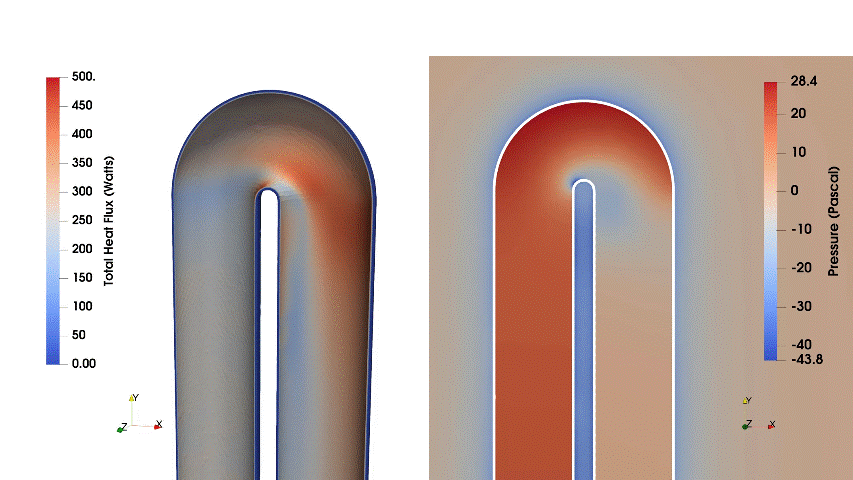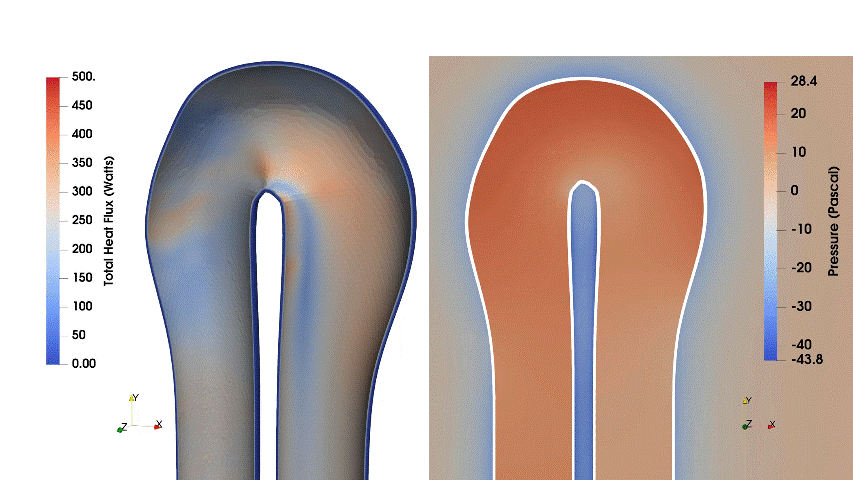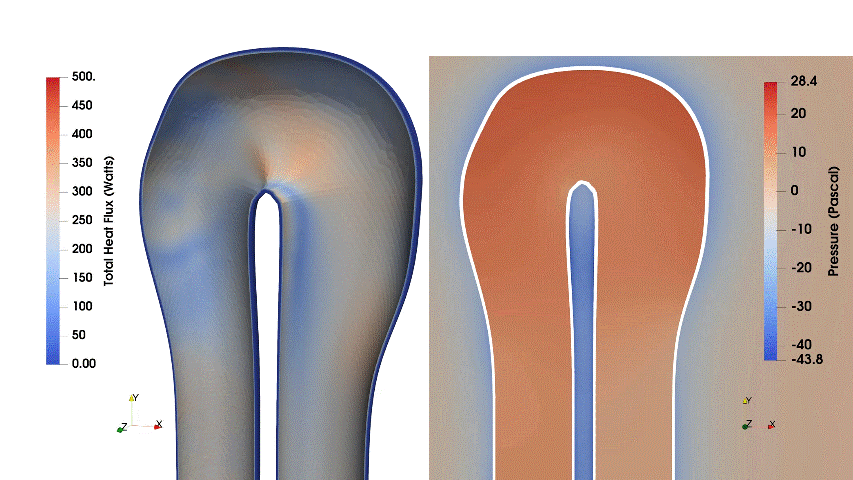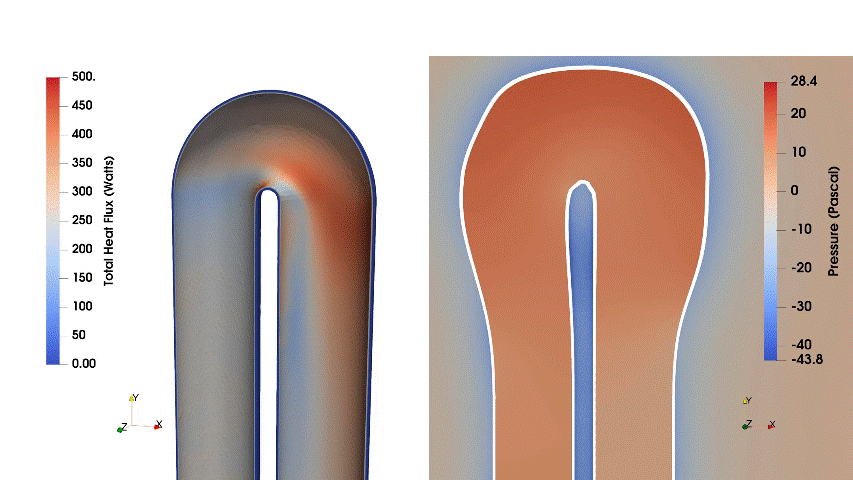
Fig. 2. Evolution of wall heat flux and velocity during the optimization